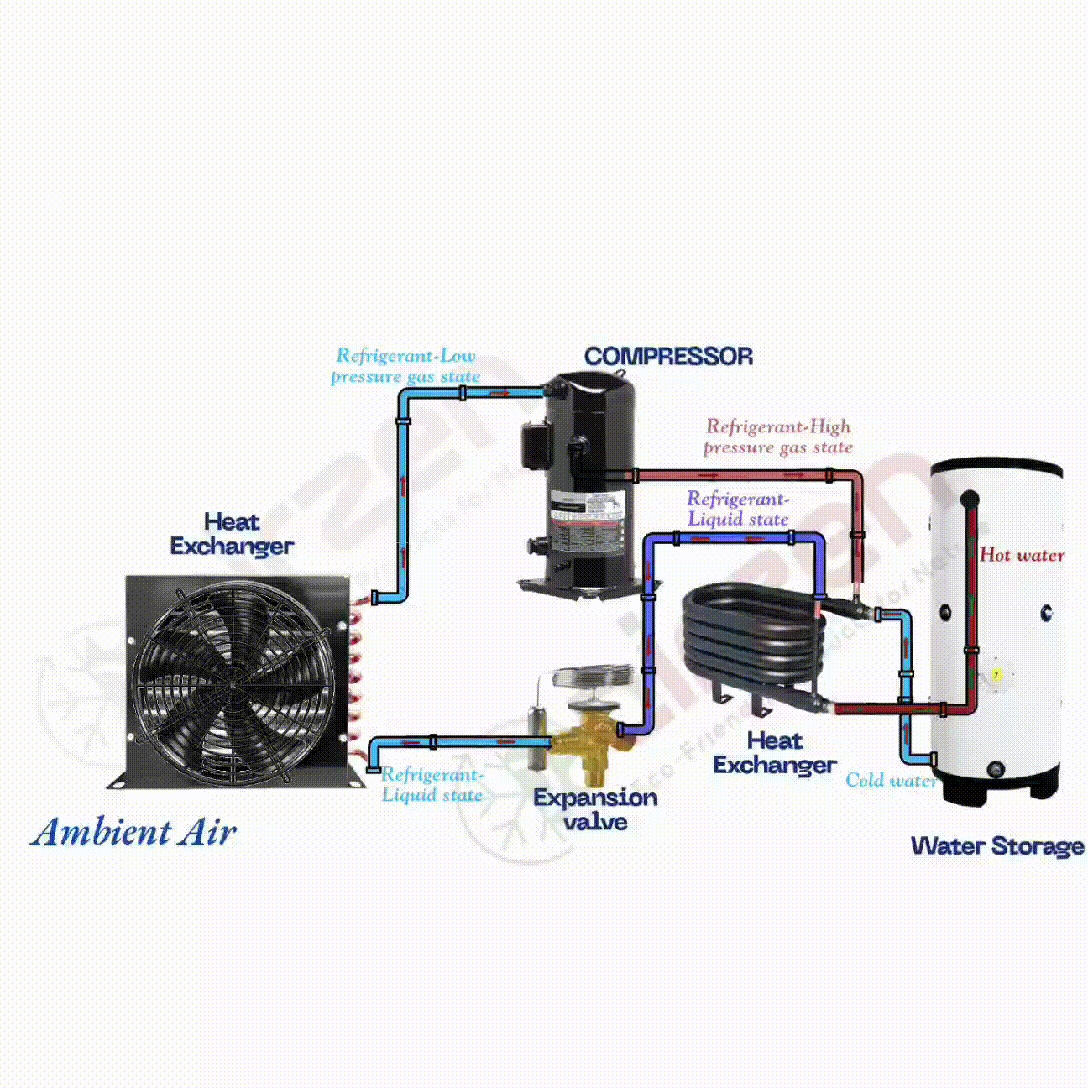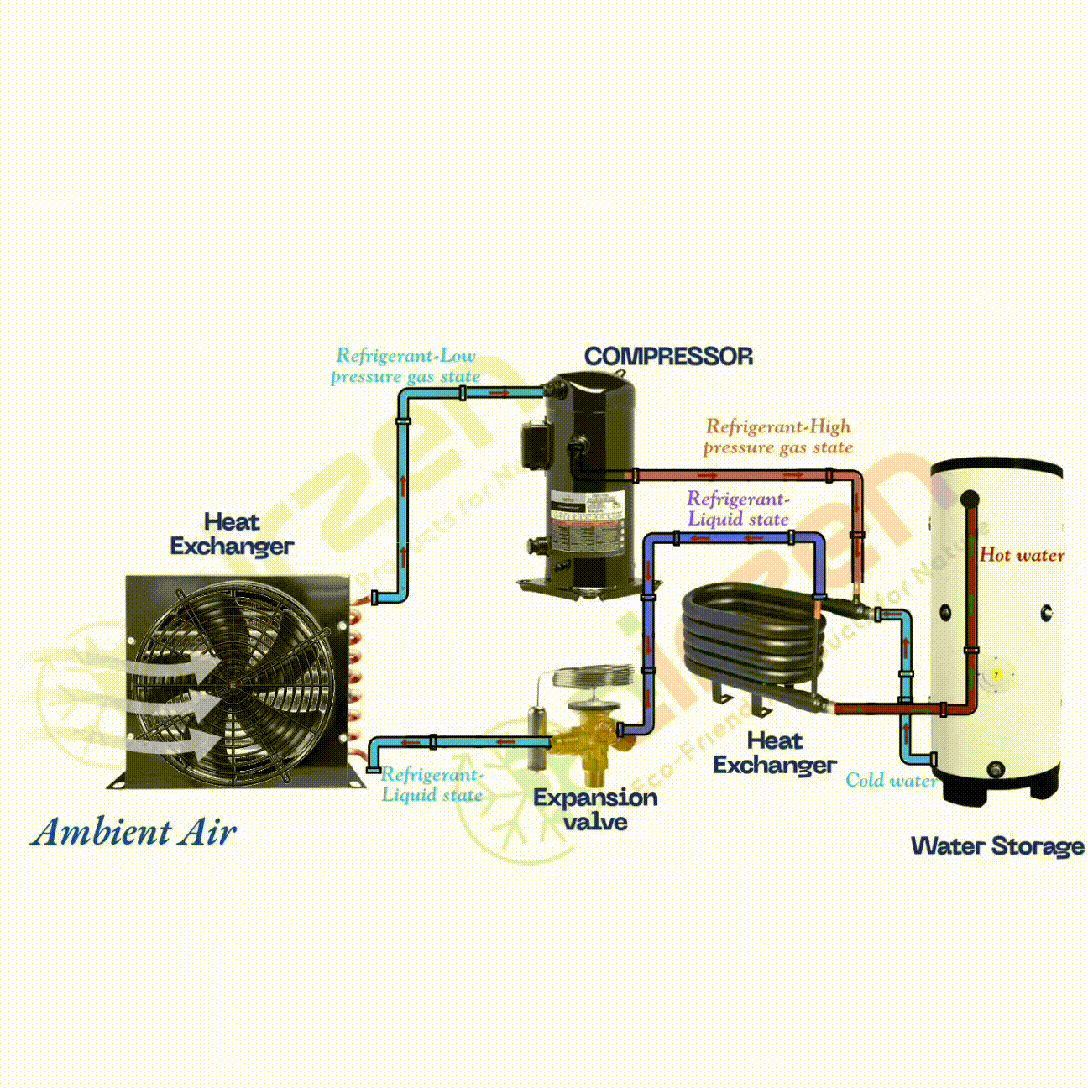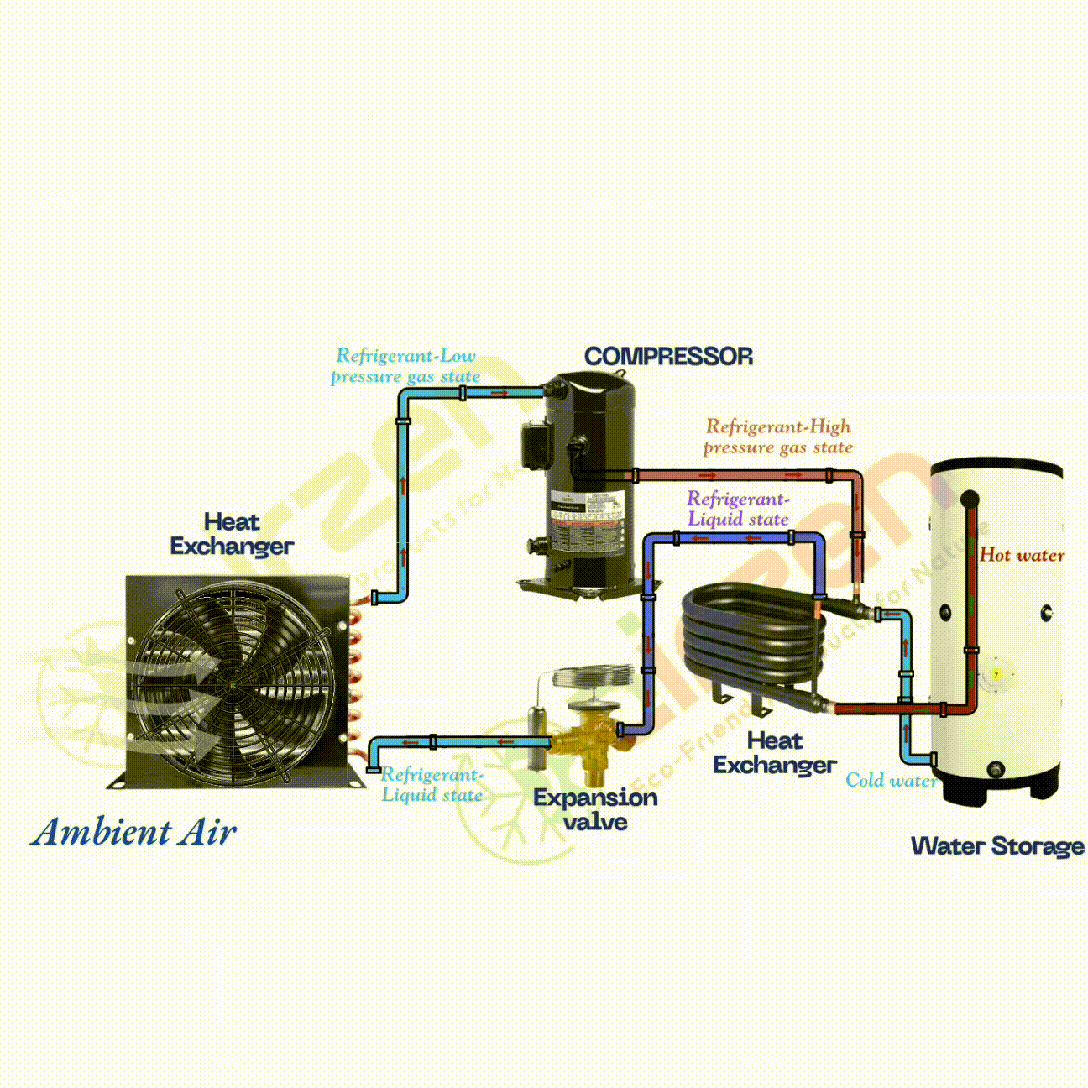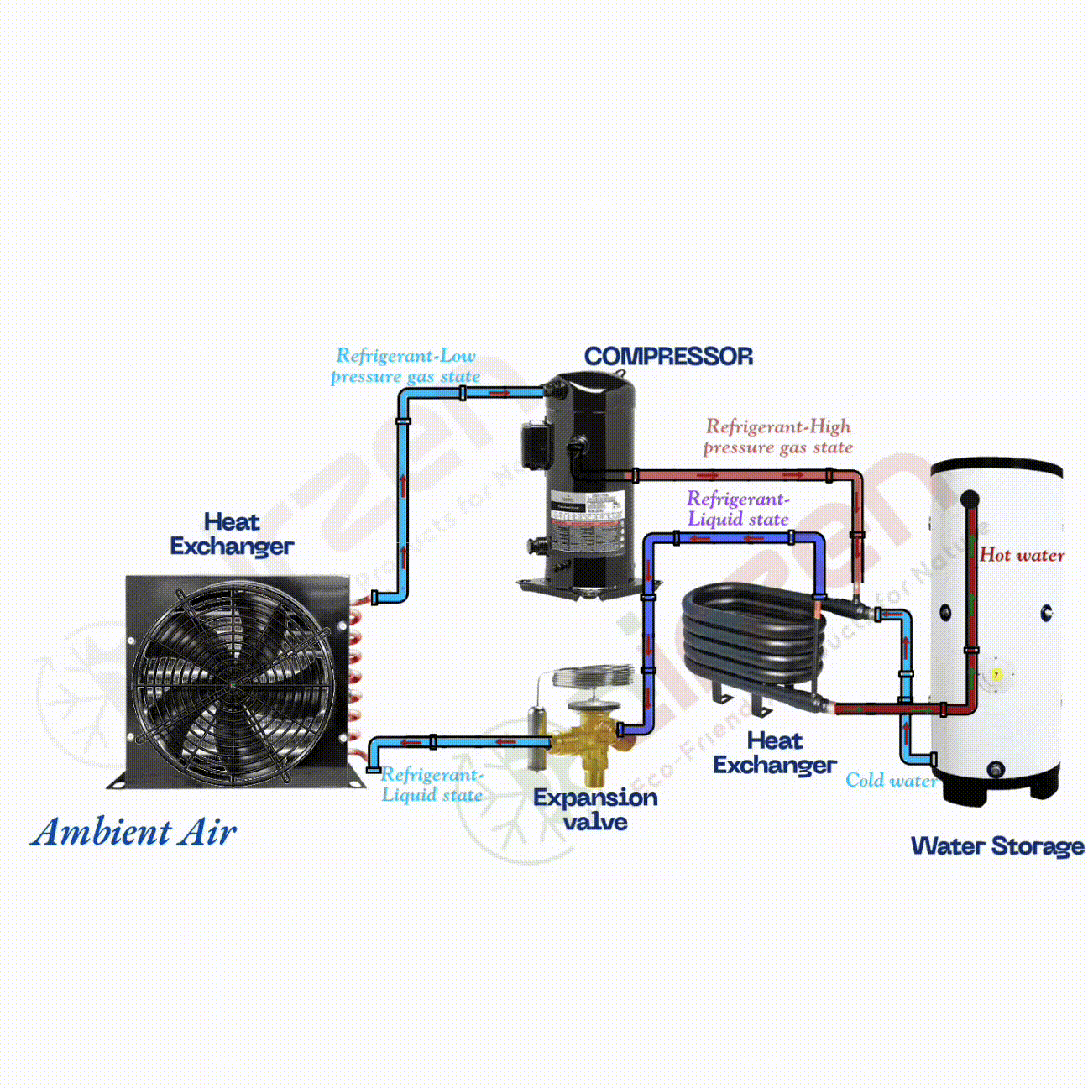
What is the role of a refrigerant in a heat pump, and how does it absorb heat energy?
The heat pump is an energy moving device The refrigerant absorbs the heat energy from ambient air.
- A heat pump is a device that moves thermal energy from one location to another, usually from a cooler area to a warmer area.
- The refrigerant is a special fluid used within the heat pump system to facilitate heat transfer.
- It operates by absorbing heat from the ambient air or another heat source, even when the outside temperature is relatively low.
- As the refrigerant absorbs heat energy, it changes its state from a liquid to a low-pressure gas, allowing efficient heat extraction.
- This process highlights the heat pump’s efficiency and its ability to utilize renewable energy sources indirectly.
How does the heat exchanger in a heat pump function, and what role does it play in energy transfer?
The heat pump is an energy moving device The refrigerant absorbs the heat energy from ambient air.
- The heat exchanger is a vital part of the heat pump system that facilitates heat transfer to the desired medium, such as water.
- After the refrigerant is compressed, it flows into the heat exchanger in its high-pressure, high-temperature state.
- The heat exchanger allows the refrigerant to transfer its heat energy to the surrounding water.
- This process cools the refrigerant while heating the water , depending on the application.
- Proper maintenance of the heat exchanger is crucial for the long-term efficiency and reliability of the heat pump.
How does the compressor in a heat pump function, and what is its importance?
The compressor uses electricity to compress the refrigerant into the high temperature and pressure.
- The compressor is a critical component of the heat pump that pressurizes the refrigerant.
- It takes the low-pressure gaseous refrigerant and compresses it into a high-pressure, high-temperature gas.
- Electricity is used to drive the compressor, making it the primary energy input for the system.
- The compression process significantly increases the temperature of the refrigerant, which is vital for effective heat transfer.
- Compressors are engineered for durability to withstand the high operational demands of the heat pump system.